As an established processor and exporter of premium quality kava, PHAMA Plus supported Lami Kava to introduce a new green kava processing method that ensures full control of post-harvest practices and quality and freshness of kava were maintained. LEARN MORE
Kava makes a significant contribution to rural livelihoods in Pacific Island producing countries.
It is an important cash crop and a significant source of income and employment for rural households and those involved in its harvesting, processing and sale. It has important cultural and social dimensions, including in Australia and New Zealand, and is used internationally for medicinal and therapeutic purposes.
In Fiji, kava is known as yaqona and is widely consumed as a beverage informally and in traditional ceremonial settings.
Why is kava a lucrative commodity?
- Fiji exported 478 metric tonnes in 2020 alone with total export earnings estimated to be around $43.6m as stated by the Fiji Yaqona Task Force.
- The volume of kava exports in the past five years was said to have increased, with 2016 recording around 259 metric tonnes, 2017 – 311 metric tonnes, 2018 – 285 metric tonnes, 2019 – 328 metric tonnes and 2020 – 478 metric tonnes as stated by the Fiji Yaqona Task Force.
- The kava GDP trend in Fiji for the past five years had consistently increased as in 2016 it was $134.5m, in 2017 it was $161.5m, 2018 it was $185.8m and 2019 it was said to be $208.2m as stated by the Fiji Yaqona Task Force.
- Kava has passed sugarcane, ginger and turmeric crop commodities in Fiji in terms of earnings as stated by the Fiji Yaqona Task Force. (Like in Vanuatu with kava surpassing commodities such as copra and cocoa)
- Kava compared with other crop commodities continued to increase and contributed to an average of 16.3 per cent of total agriculture GDP for the past five years as stated by the Fiji Yaqona Task Force.
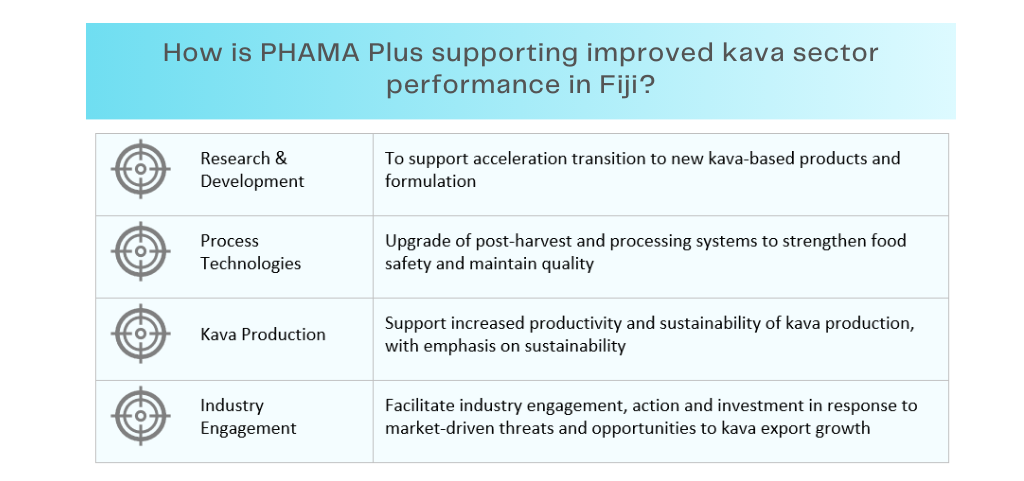
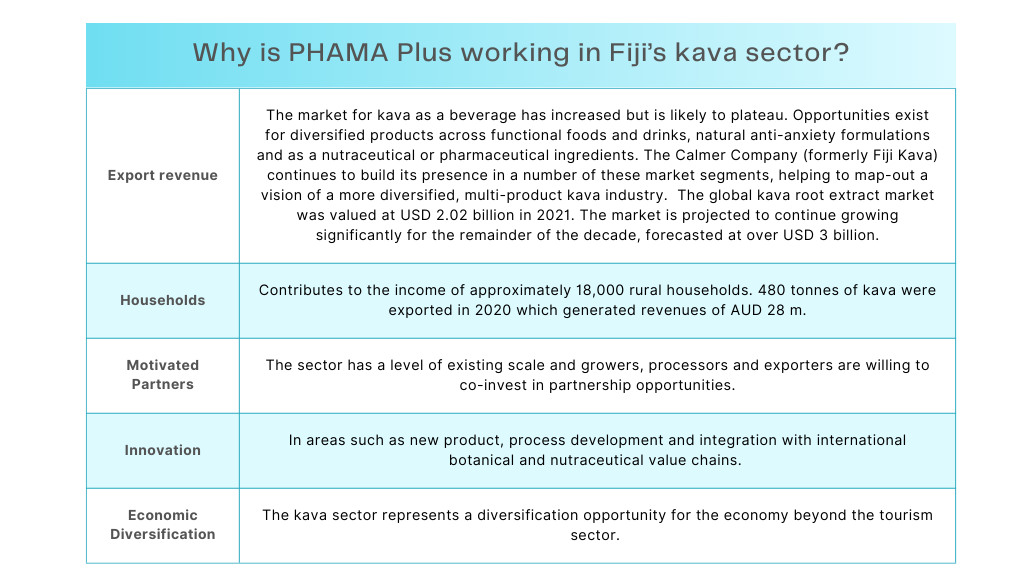
For more information, please reach out to PHAMA Plus Country Manager Fiji Navitalai Tuivuniwai on n.tuivuniwai@phamaplus.com.au.
